km2 wetlands worldwide
(Ramsar, 2021)
The world's mangroves store carbon equivalent to over 21 gigatons of CO2, prevent more than $65 billion in property damages, and reduce flood risk to some 15 million people yearly.
What we do






Blue & teal carbon
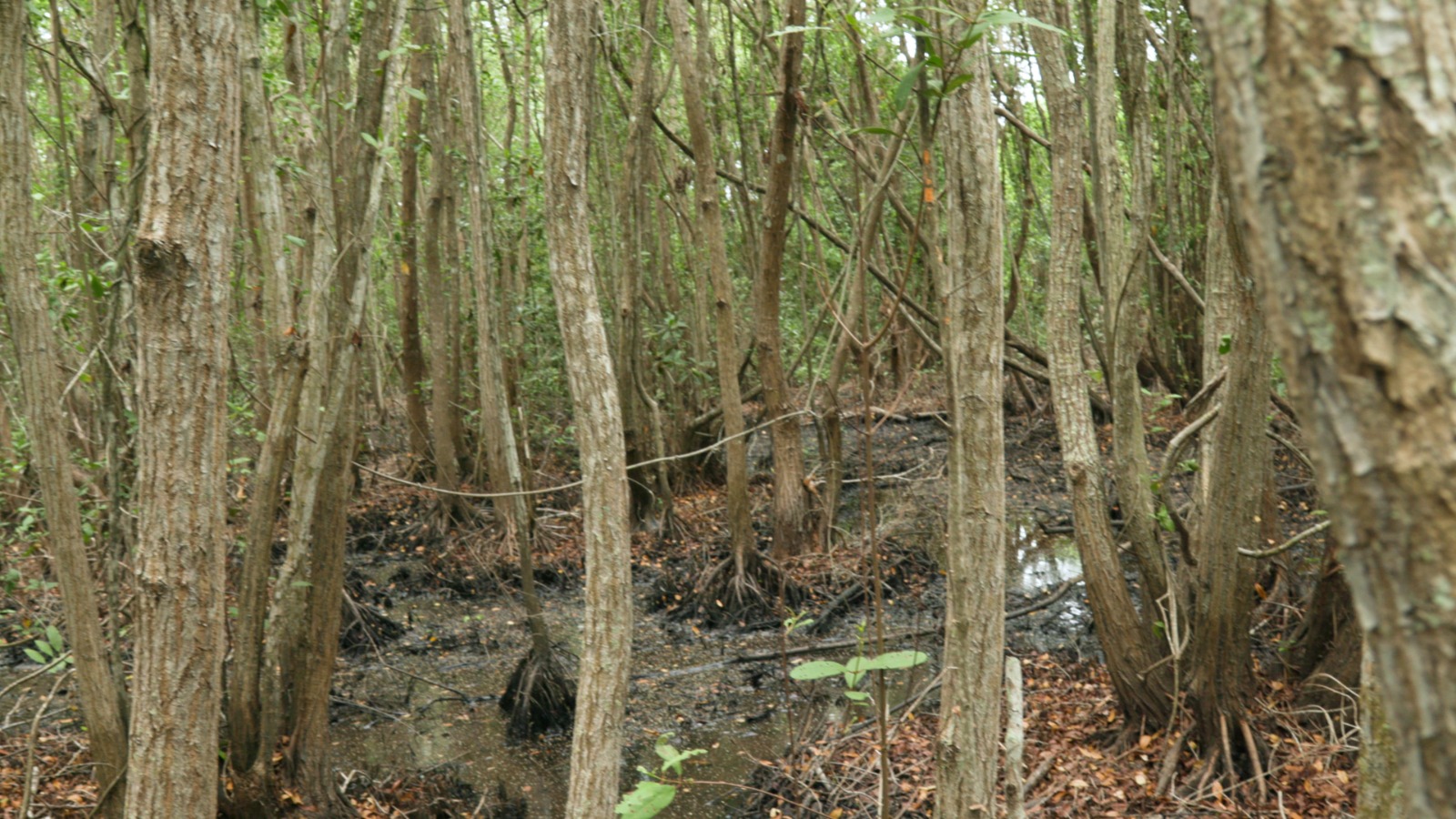
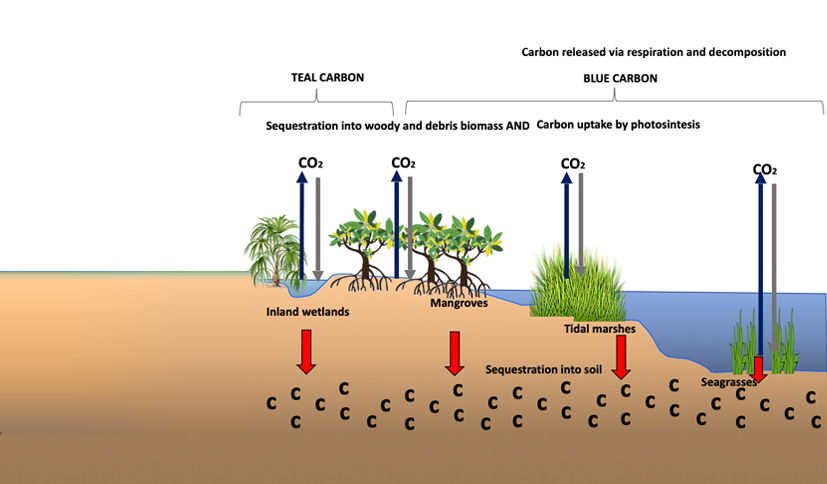
Blue carbon is the carbon stored in coastal and marine ecosystems. Coastal wetlands, including seagrass meadows, mangroves and tidal marshes, are major blue carbon ecosystems and are often termed “blue forests”.Teal carbon is the carbon stored in inland freshwater (non- tidal) wetlands. Equivalent to coastal wetlands, they have the capacity to regulate greenhouse gases. However, their degradation due to land-use change, pollution, water extraction, and landscape modification can release high levels of carbon dioxide and methane back into the atmosphere.
Capture & storage of carbon
The process of removing carbon from the atmosphere and depositing it in a reservoir. The conservation, management, and restoration of ecosystems such as forests, peatlands, wetlands, and grasslands have the potential of capturing and storing large amounts of carbon dioxide each year. This process is largely artificial or 'direct', representing an effective way of neutralizing emissions put into human practices, such as manufacturing or construction.
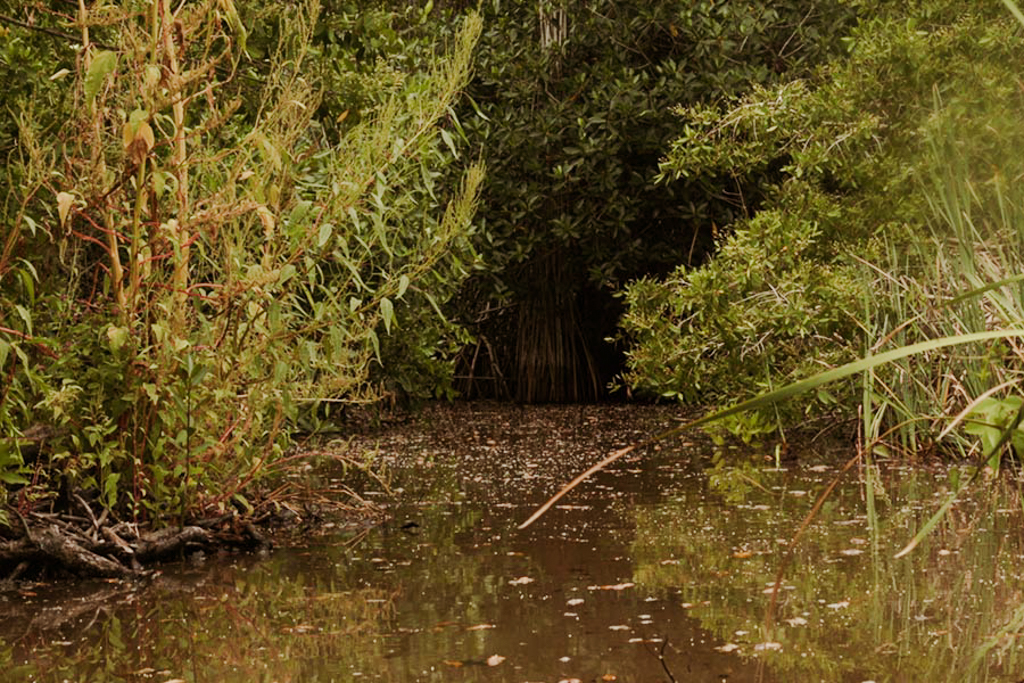

Captures 4x more carbon than rainforests
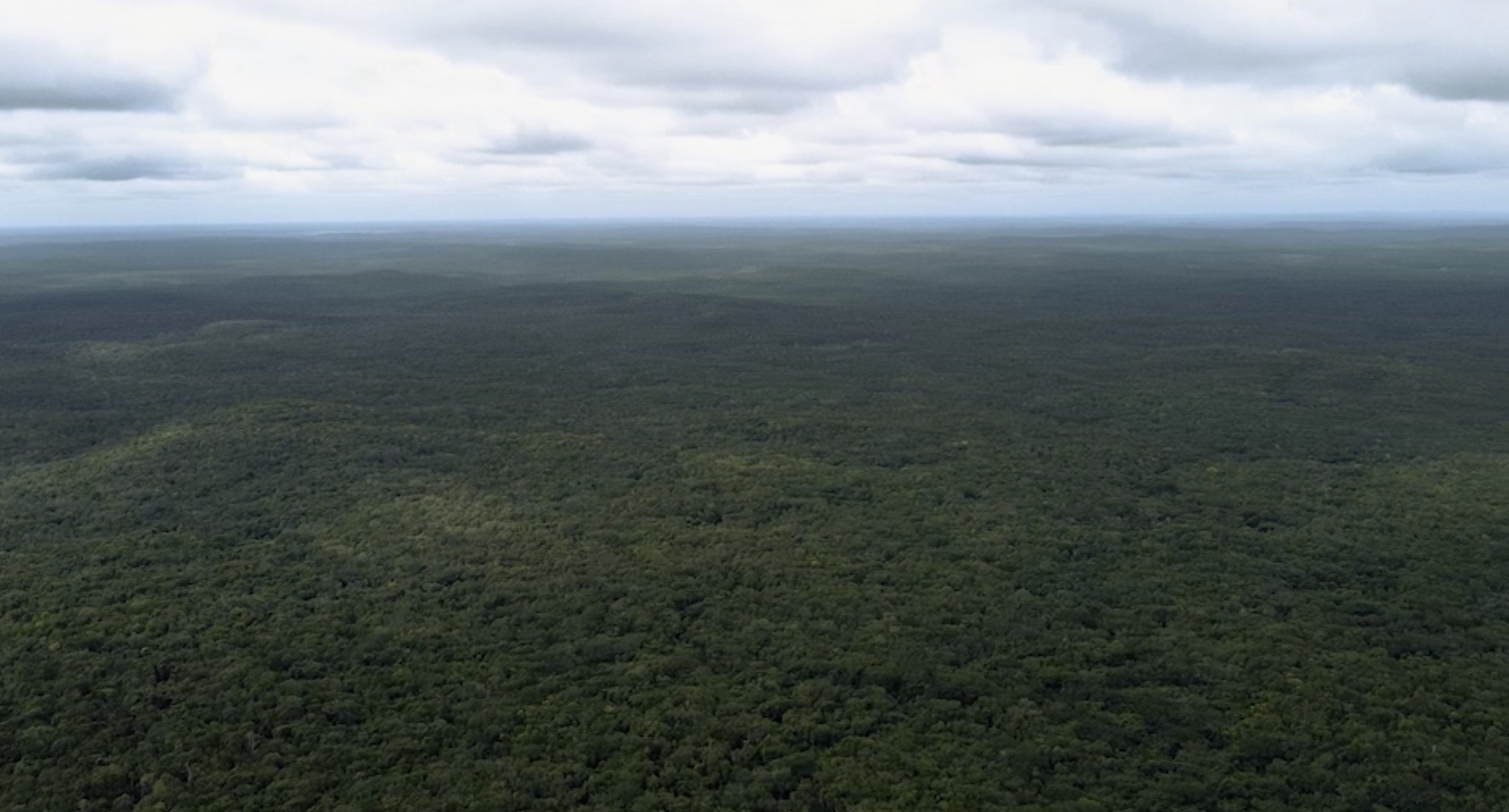
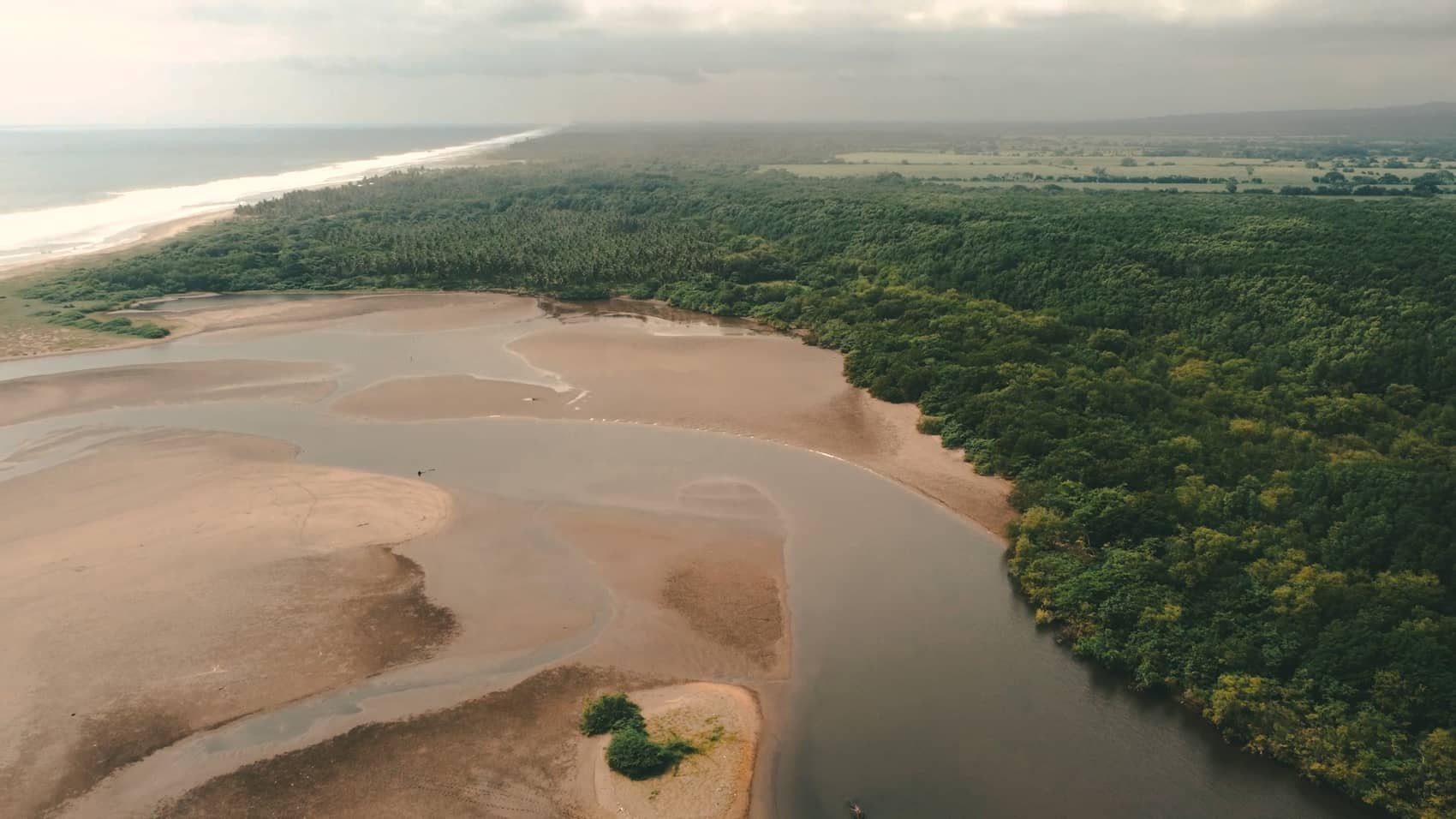
Mangroves provide globally important ecosystem services and carbon sequestration and are thus an important habitat to conserve and repair when possible. Mangroves are naturally disturbed by floods, tsunamis, coastal storms like cyclones and hurricanes, lightning, disease and pests, and changes in water quality or temperature. Mangrove forests are responsible for approximately 10% of global carbon burial.
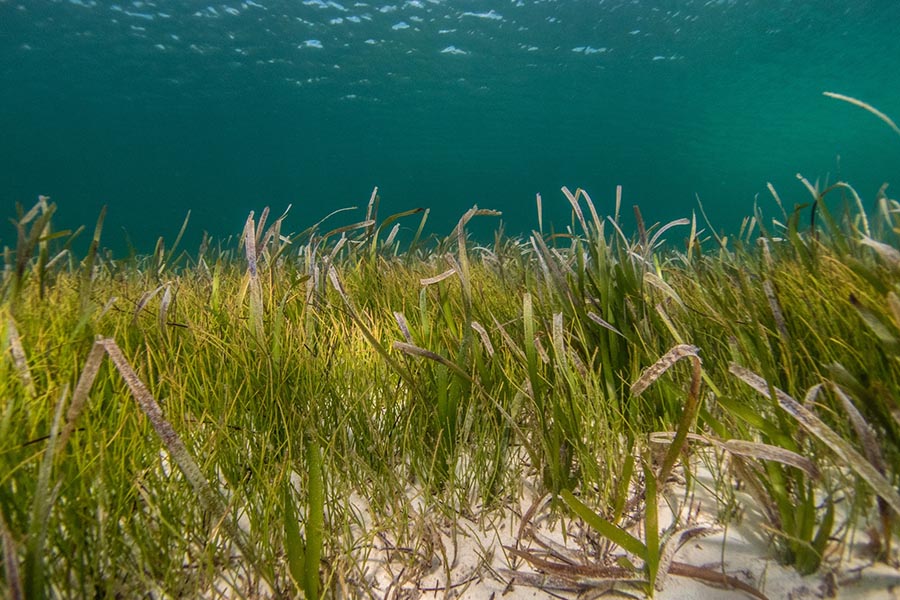

35x faster than the rainforest carbon sequestration
These seagrass meadows are highly productive habitats that provide many ecosystem services, including sediment stabilization, habitat and biodiversity, better water quality, and carbon and nutrient sequestration. Although seagrass makes up only 0.1% of the area of the ocean floor, it accounts for approximately 10–18% of the total oceanic carbon burial.
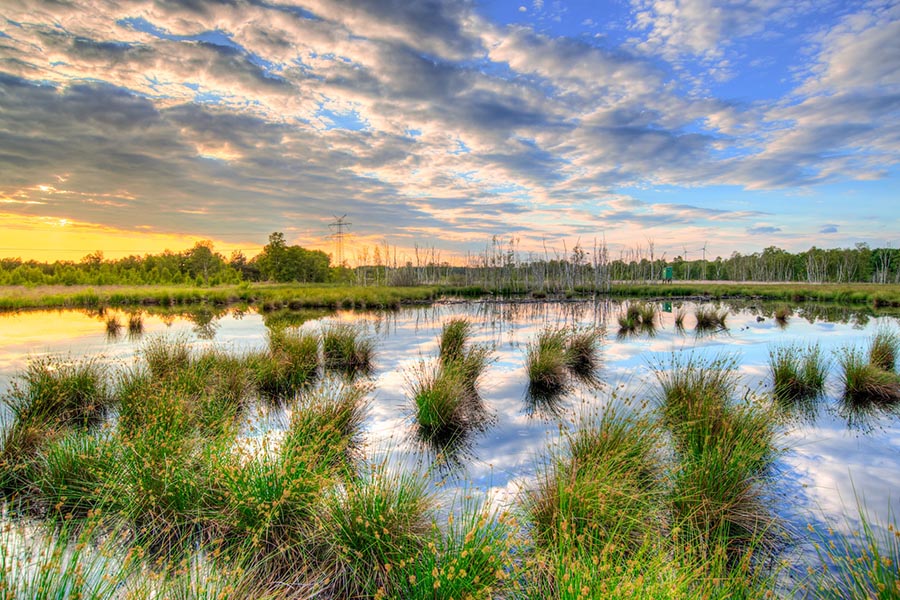

Captures carbon & traps sediment for runoff
Marshes have high productivity, with a large portion of primary production in belowground biomass. Marshes provide valuable habitat for plants, birds, and juvenile fish, protect coastal habitat from storm surge and flooding, and can reduce nutrient loading to coastal waters. Salt marshes cover approximately 22,000 to 400,000 km2 globally, with an estimated carbon burial rate of 210 g C m−2 yr−1.
Mangroves can capture four times more carbon than rainforests can. With the rising greenhouse gases including CO2, mangroves have become an essential tool in fighting climate change.
Pablo's Story
Our projects
We protect and conserve nature, while providing co-benefits so wetland landowners can thrive.In Mexico
Land ownership and the exploitation of native farmworkers have historically been at the center of every conflict in Mexico.Zere's success depends on developing a reliable systematic process to bring carbon credits to market that is trustworthy, dependable, and built to service the interest of our landowning partners.
Our team
We work to improve communities in wetlandsPablo Granados
Environmental Champion / Co-FounderMaría Luisa (Malú) Villarreal Sonora
Chief Scientist / Programme DesignerAlberto Osegueda
Legal & Financial Compliance / Co-FounderEduardo Celis Rojo
Managing Partner / Co-FounderAmparo Granados
Program CordinatorGils Aubry
Board AdvisorMarilupe Reyes Retana
Senior Corporate Legal Counsel
CLAUDIA ALCARAZ
Communication and Marketing
EDUARDO GONZALEZ
Commercial development

 Sequestration
Sequestration Mangroves
Mangroves Seagrass
Seagrass Marsh
Marsh



















